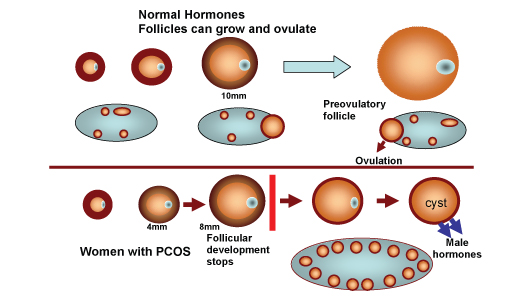
The type of birth control you use is a personal decision, and there are many options to choose from. If you’re a sexually active person who can become pregnant, you could consider birth control pills.
In this article, we share all you need to know about one of the most common birth control pill brands in Singapore — Diane-35®:
- How it works;
- How to take it;
- What to do if you missed a dose;
- Potential side effects; and
- Where to buy Diane-35® in Singapore.
What Is Diane-35®?
Diane-35® is a brand-name combination birth control pill that contains 2 hormones:
- progestogen (2mg cyproterone acetate); and
- estrogen (0.035mg ethinylestradiol).
Estelle® is a generic version of the brand-name drug Diane-35®.
Besides preventing unwanted pregnancies, Diane-35® can also help to:
- regulate periods
- prevent anaemia by making periods lighter or shorter
- lessen menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea)
- manage symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysmorphic disorder (PMDD)
- treat symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- treat endometriosis or uterine fibroids
- lower the risk of ovarian cancer, uterine cancer and colon cancer
- treat moderate to severe acne related to androgen sensitivity
- stop unwanted hair growth (hirsutism)
- reduce migraines
- control hot flashes during the transition into menopause
How Does Diane-35® Work?
Diane-35® helps to prevent pregnancy by:
- Inhibiting ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovary;
- Thickening the cervical mucus (the fluid in the vaginal tract), hindering the sperm from reaching the egg to fertilise it.
How Effective Is Diane-35®?
Diane-35® has shown to be highly effective in preventing pregnancy. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, when used perfectly Diane-35® is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. Even with typical use (possibly due to missed pills or improper storage), Diane-35® is still around 91% effective.
In general, birth control pills are more effective than male condoms in preventing pregnancy — male condoms are shown to be 98% effective when used perfectly, and 82% effective with typical use. However, unlike male condoms, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) cannot be prevented by using birth control pills.
Therefore, always use dual protection of condoms and non-barrier contraceptives such as birth control pills during any sexual activity.
How To Take Diane-35® Birth Control Pills?
Diane-35® contains 21 active pills. You should take one pill at the same time every day for 21 days, followed by 7 days where you take no pills. During the pill-free days, a withdrawal bleed usually occurs that is similar to having your period. After the 7-day pill-free interval, start on a new pack of Diane-35® whether or not you have any menstrual bleeding.
You should swallow each pill whole with water. Do not chew the pill. The back of the pill strip states the days of the week (Monday – Sunday). Start your course by taking a pill marked with the correct day of the week and follow the direction of the arrows on the strip.
What To Do If I Missed My Diane-35® Birth Control Pill?
You should establish a regular routine of taking your birth control pills at the same time every day during the 21 days. This is because taking a pill late or missing pills may affect the effectiveness of the pill in preventing pregnancy.
Diane-35® is considered “missed” if you:
- don’t take it for 24 hours or more after you were supposed to; or
- vomit or suffer from diarrhoea within 3 to 4 hours of pill-taking.
If you forget to take a pill, here’s what you should do:
If you are late (less than 24 hours) or missed (24 to 48 hours) an active pill
You’re still protected against pregnancy if you missed 1 pill anywhere in the pack or started a new pack 1 day (24 hours) late.
Follow these steps:
- Take the late or missed pill immediately
- Continue taking the remaining pills at the usual time (even if it means taking two pills on the same day)
- Take the 7-day pill-free break as prescribed or if you’re on an everyday pill, take the inactive pills
- Emergency contraception is not usually needed but can be considered if hormonal pills were missed earlier in the cycle or in the last week of the previous cycle
- No additional contraceptive protection (e.g. condoms) needed
If you missed two or more active pills (48 hours or more)
When this happens, it greatly increases your chances of ovulation. In this case, when you missed 2 or more active pills anywhere in the pack or started a new pack only after 2 days (48 hours) or more, you may not be protected against pregnancy.
What you should do:
- Take the last pill that you missed immediately even if it means taking 2 pills a day
- Discard any earlier missed pills
- If the missed pill is within:
- Week 1 (pills 1 to 7) or Week 2 (pills 8 to 14) of the pack:
- Continue to take the active pills in your current pack daily
- Take a 7-day break
- Begin a new pack the next day
- Week 3 of the pack (pills 15 to 21):
- Continue to take the active pills in your current pack daily
- When you have finished taking all the active pills, discard the pack
- Don’t take the 7-day break, begin a new pack the next day
- Week 1 (pills 1 to 7) or Week 2 (pills 8 to 14) of the pack:
- Consider taking emergency contraception if you missed 2 or more pills during the first week of a pack and/or had unprotected sex in the last 7 days
- Use extra contraception (i.e. condoms) or abstain from sex for the next 7 days
What Are The Potential Side Effects Of Diane-35®?
Women who just started taking Diane-35® may experience some of the following side effects:
- Nausea, vomiting, bloating and stomach cramps. Take Diane-35® after food to reduce these side effects.
- Headache. Can be managed by taking over-the-counter painkillers such as Paracetamol.
- Spotting between your periods during the first few months of taking oral contraceptives.
- Breast tenderness
- Weight changes due to fluid retention, mood swings. Take Diane-35® at the same time every day to avoid huge changes in the hormone levels in your body.
Side effects vary widely among individuals and usually ease within 2–3 months of starting to take the pill as your body adjusts to the hormones. Inform your doctor if the side effects last for a long time (more than 3 months) or bother you.
How To Buy Diane-35® In Singapore?
In Singapore, all hormonal birth controls including Diane-35® can only be purchased if you have a valid prescription from a registered doctor and are unavailable over-the-counter. In other words, you will have to set aside some time amidst your busy schedule to visit the general practitioner or gynaecologist in person.
Siena is a digital health clinic that offers you easy and affordable access to birth control. Simply complete an online questionnaire, and speak with a doctor online from the comfort of your home. If prescribed, we deliver your birth control to you in discreet packaging at no additional charge.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014, April). Appendix D: Contraceptive Effectiveness. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr6304a5.htm
- HealthHub. (2019, September). Cyproterone acetate / Ethinylestradiol. https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/medications/310/Cyproterone-acetate-Ethinylestradiol
- NPS MedicineWise. (2021, January). Diane-35 ED. https://www.nps.org.au/medicine-finder/diane-35-ed-tablets
- Pharmaceutical Society of Singapore. (2021. January). Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (21-day regimen). HealthHub. https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/medications/443/Combined-Hormonal-Contraceptives-21-day-regimen